A Red Giant Has Which of the Following
Hydrogen and carbon D. The more massive the star is the faster it burns its fuel d.
A giant star that has a relatively low surface temperature giving it a reddish or orange hue.
. Play this game to review Science. Red giants are made of carbon and oxygen throughout which escape more easily Really massive stars differ from stars with masses like the Sun in that they can fuse elements beyond carbon and oxygen in their hot central regions. The life cycle of a low mass star left oval and a high mass star right oval.
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a red giant. Carbon and oxygen c. All stars evolve the same way up to the red giant phase.
They are not massive stars but rather late expanded stages of lower-mass main-sequence stars that have exhausted the hydrogen in their core and are fusing their remaining. The amount of mass a star has determines which of the following life cycle paths it will take after the red giant phase. A red giant stars appearance is usually from yellow-orange to red including the spectral types K and M but also S class stars and carbon stars.
Question 51 Which of these is NOT a feature of white dwarf stars. Red dwarfs are less common than giants and live longer. A region on the H-R diagram where stars have roughly the same luminosity.
Which of the following has the longest life. The average star has shorter life span C. Main sequence star B.
No elements heavier than iron can be produced in a massive star. The illustration above compares the different evolutionary paths low-mass. The core of red giant star is made up of carbon b.
The core of red giant star is made up of carbon B. The neutron star radius. Which of the following is a star that has begun to run out of fuel.
Which of the following gases are major components of star. The average star has shorter life span c. Helium to carbon helium to hydrogen hydrogen to helium hydrogen to carbon.
The core of red giant star is made up of carbon B. Which of the following best describes a nebula. However astronomers have found a number of gas giant exoplanets orbiting close to their red giant stars.
Noun a star that has low surface temperature and a diameter that is large relative to the sun. All stars evolve the same way up to the red giant phase. The Red Giant is redder than the Main Sequence star.
Which of the following is true for Red Giant with the same surface temperature as a Main Sequence star. Which of the following best describes the relationship between red dwarfs and giant stars. The horizontal branch is a.
Preview this quiz on Quizizz. Helium and carbon d. Red giants are non-main-sequence stars positioned in the upper right of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram.
Extended outer layers b. Dwarf star sun. The region around a black hole where everything is trapped and nothing can get out to interact with the rest of the universe is called _____.
Why is a 1 solar-mass red giant more luminous than a 1 solar-mass main sequence star. In the core of the red giant helium fuses into carbon. Helium has accumulated in the core and hydrogen is now undergoing nuclear fusion in the outer shells.
A red supergiant is an aging giant star that has consumed its cores supply of hydrogen fuel. The star has now reached the red giant phase. Red dwarfs burn energy faster than giants and have shorter lives.
It is a subgiant that grows in luminosity until helium fusion begins in the central core. Hydrogen and helium 6. The average star has shorter life span C.
Hydrogen and carbon b. Its radius is about the same as the Earth. The Red Giant is less luminous than the Main Sequence star.
Red giant stars usually result from low and intermediate-mass main-sequence stars of around 05 to 5 solar masses. A red giant star is a dying star in the last stages of its stellar evolution. The gravitational redshift zone.
It is made up mostly of hydrogen and helium. Which of the following statements is FALSE. The more massive the star is the faster it burns its fuel D.
Neutron star Red giant Stellar nebula White dwarf 2 See answers Advertisement Advertisement queenie654 queenie654 I think it is the red giant Advertisement Advertisement umkitty umkitty Answer. Which of the following statements is FALSE. A region on the H-R diagram where stars have roughly the same temperature.
These so-called hot Jupiters have managed to. Fusion reactions are producing energy at a greater rate in the red giant. O a non-fusing carbon core O a radius comparable to the Sun a.
Our own sun will turn into a red giant expand and engulf the inner planets possibly even Earth. Carbon and oxygen B. The Red Giant is more luminous than the Main Sequence star.
The amount of mass a star has determines which of the following life cycle paths it will take from there. Which of the following describes a star with a hydrogen-burning shell and an inert helium core. It is red because it is cooler than it was in the main sequence star stage and it is a giant because the outer shell has expanded outward.
Red giant stars are normal main sequence stars that are formed due to the loss of their hydrogen supply which causes their outer layer to become inflated and to expand hugely and their surface temperature to reduce to as low as 5000 K. Cool surface temperature 28. Question 48 A red giant has which of the following.
Which type of fusion occurs in the red giant phase of the demise of a sunlike star. Which of the following statements is FALSE. Helium and carbon C.
The Red Giant has a smaller radius than the Main Sequence Star. It has a mass of roughly half the mass of the Sun. Which type of telescope would you need to easily see a potential.
A red giant star is a dying star in the last stages of stellar evolution. Red giant stars have an intermediate or low mass. Red super giant D.
A red giant is a luminous massive star that is in a late phase of stellar evolution.

Effects Of The Solar Geomagnetic Storm Are Still Being Felt On Earth In 2021 Geomagnetic Storm Storm Solar
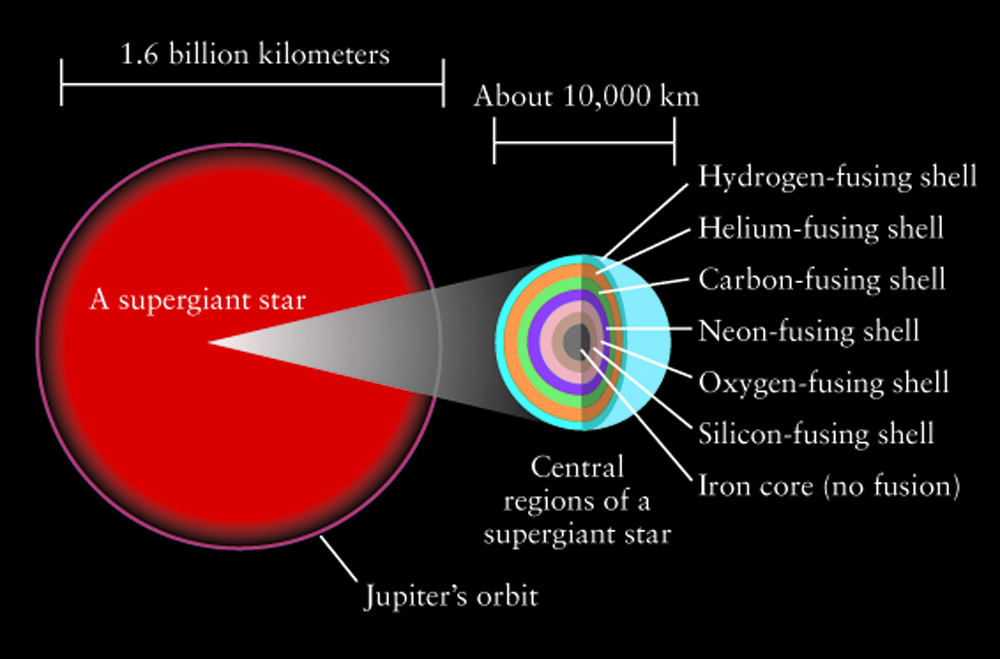
Lecture 18 Evolution Of High Mass Stars

Pin By Cheryl C On God S Awesomeness Matter Science Earth Astrophotography

Star Lash White Dwarf Literally Whipping Red Dwarf Video Red Dwarf Red Giant Stars

Https Upscaleexistence Blogspot Com What Is To Become Of Our Species Mind Blowing Space Facts About The Universe Space Facts Science Facts Astronomy Facts

Big Red Giant This Morning Red Giant Celestial Sunset

Evolution From The Main Sequence To Red Giants Astronomy

It S Alive Dead Star Reawakened By Red Giant Companion Gravitational Waves Neutron Star Pulsar

Evolution From The Main Sequence To Red Giants Astronomy

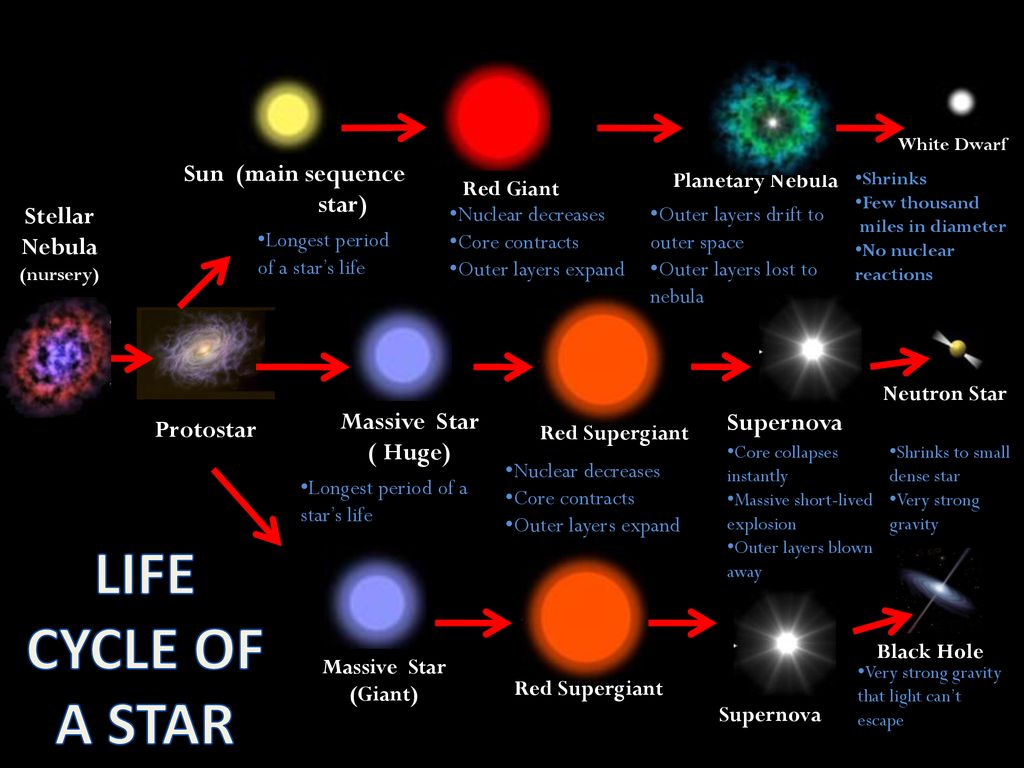
Life Cycle Of A Star Sun Main Sequence Star Stellar Nebula Ppt Download
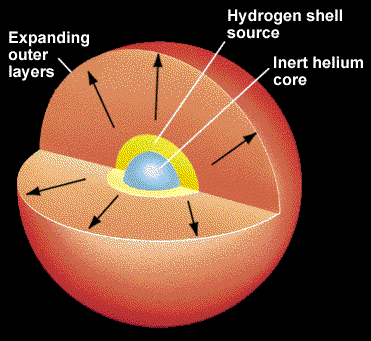
Lecture 17 Evolution Of Low Mass Stars

Types Of Stars What Kind Of Star Is The Sun Beauty Above Us Https Youtube Com Watch V E7wapzpdy4c Neutron Star Stars Astronomy
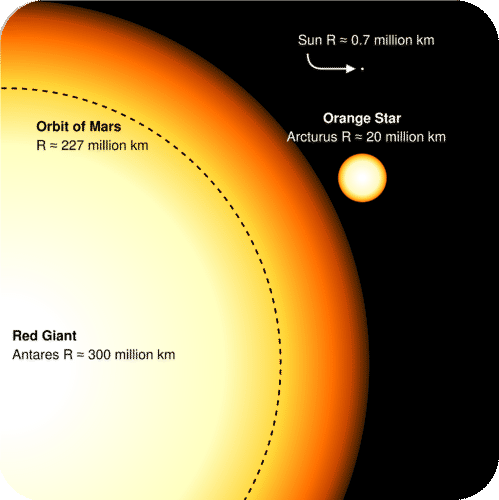
Life Cycles Of Stars Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation

Touch This Image Red Giant Stars Facts Definition The Future Of The Su By Brittany Mills Star Life Cycle Life Cycles Black Hole

Life Cycle Of A Star By Pierce Life Cycles Star Life Cycle Earth Science Projects


Comments
Post a Comment